The soil, vegetation and the lower atmosphere are key compartments of the Earth, where almost all activities of mankind take place. This region is characterized by extremely complex patterns, structures and processes that act at different time and space scales. While the exchange of energy, water and carbon is continuous between the different compartments, the pertinent fluxes are strongly heterogeneous and variable in space and time. Therefore, the quantitative prediction of the systems behavior constitutes a major challenge to scientists and policymakers, especially in view of global climate change.
 Project D2
Project D2
Experimental study of spatio-temporal structures in atmosphere-land surface energy, water and CO2 exchange
 Project C1
Project C1
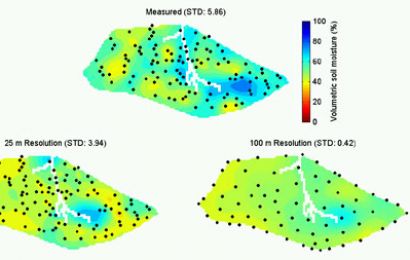
Eco-hydrological investigations of the feedback between the biosphere, pedosphere and the hydrosphere at different spatial and temporal scales
 Project Z3
Project Z3
Measurement support and data processing
 Project A3
Project A3
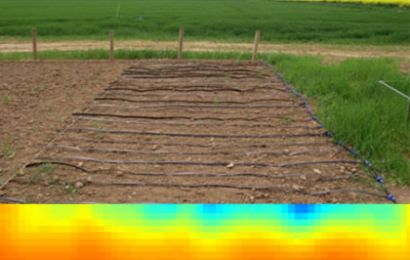
Inverse modelling of soil hydraulic property patterns from non-invasive electrical measurements
 Project A4
Project A4
Multiphase flow simulations coupled to NMR and SIP signatures in reconstructed natural porous media using Lattice Boltzmann methods
Traditionally, the scientific disciplines, such as geophysics, soil and plant science, hydrology and meteorology have focused with success on their respective compartments. The interaction of different compartments, however, poses many open questions which are the research topic of this initiative. We are interested in the specific role of patterns and structures of physical and chemical properties and fluxes in the behavior of the soil-plant-atmosphere system at various spatiotemporal scales. We hypothesize that the explicit consideration of patterns and structure will lead to a common methodology that will increase our understanding and predictive capabilities of the soil-vegetation-atmosphere system. Research groups in the field of soil and plant science, remote sensing, hydrology, meteorology and mathematics located at the Universities of Aachen, Bonn, and Cologne and the Research Centre Jülich study the soil-vegetation atmosphere system under this new paradigm.
Thus, we first have to improve our knowledge about the mechanisms leading to spatial and temporal patterns in energy and matter fluxes of the soil-vegetation-atmosphere system. In the field, patterns are monitored continuously using existing and novel geophysical and remote sensing techniques from the local to the catchment scale based on ground penetrat ing radar methods, induced polarization, radiomagnetotellurics, electrical resistivity tomography, boundary layer scintillometry, lidar techniques, microwave radiometry, and precipitation radars with polarization diversity. State-of-the art simulation and data assimilation tools are currently evaluated, improved and integrated in a general modeling concept under the novel holistic paradigm of patterns.